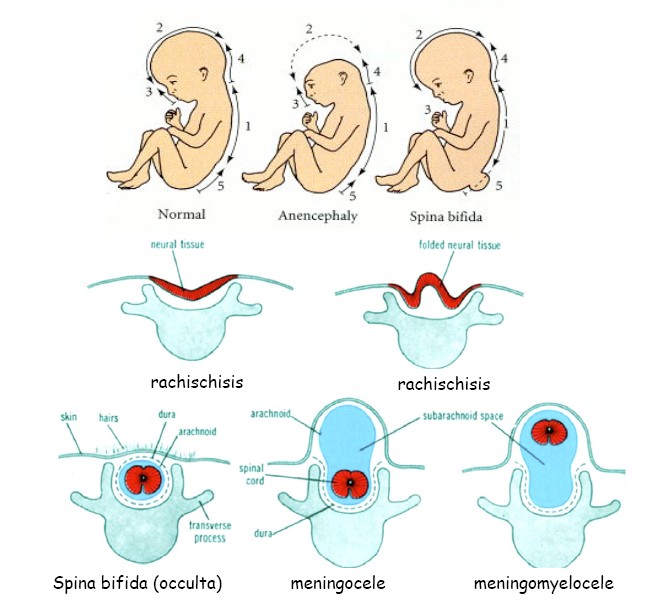
 Neural tube defects are congenital birth defects in the spinal cord, brain, and spine. They are one of the more common birth defects and affect over 300,000 babies every year all over the world. One of the resulting conditions, spina bifida occurs in about 1,500 babies born yearly in the United States alone.
Neural tube defects are congenital birth defects in the spinal cord, brain, and spine. They are one of the more common birth defects and affect over 300,000 babies every year all over the world. One of the resulting conditions, spina bifida occurs in about 1,500 babies born yearly in the United States alone.
The defect happens very early in pregnancy before the mother even has a positive pregnancy test. The more common types includeancephaly (no brain or skull) and spina bifida (protrusion of the spinal column). There is also a few less common type known as chiari malformation that is a protrusion of brain tissue down into the spinal column and encephaloceles (parts of the brain tissue protrudes through the skull). Read on to learn more about neural tube defects and how to prevent them.
What Causes Neural Tube Defects?
In general, the cause of neural tube defects is still unknown. There are a few factors that may contribute to the defects including nutritional status of the mother, genetics, and lifestyle factors. There is research that shows the following groups may have increased risks of having a baby with neural tube defects, including:
- Diabetic mothers with poor sugar control
- Mothers on seizure medications
- Exposure to high temperatures early in pregnancy
1. Folic Acid Deficiency
While it isn’t actually the folic acid deficiency that causes neural tube defects, taking folic acid can decrease the incidence of gene mutations that lead to the defects. Folic acid is one of the B vitamins and research shows that when women get enough of this and other B vitamins before pregnancy and in early pregnancy, the occurrence of neural tube defects decreases dramatically than in those who didn’t get enough folic acid. Check here to learn more essential things to do before getting pregnant.
2. Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
There is some evidence to suggest that certain environmental and lifestyle factors can contribute to higher numbers of these defects including exposure to secondhand smoke or the mother smoking, obesity in the mother, diabetes, and drugs that inhibit folic acid (methotrexate).
3. Related Genetic Syndromes
Two types of genetic syndromes are associated with more cases of neural tube defects and are not related to folic acid deficiency. Infants born with Meckel Syndrome and Triploid Syndrome can also have associated issues in the neural tube. These conditions are very rare.
How Is Neural Tube Defect Treated?
The treatment for defects in the neural tube depends on what area is affected, the severity, and the type of defect. Some are treatable and some are not. When an infant is born with anencephaly (little or no brain and skull) there is no treatment and they usually only live to a few hours to days. This is the most severe type of neural tube defect.
- Surgical Intervention. The other less severe types are usually surgically treated to repair the protrusion of brain tissue or spinal cord contents and close up any openings. Doctors can also perform these surgeries while the fetus is still in the mother’s womb if done before the 26th week of pregnancy.
- Shunting.Doctors can also place a shunt to help relieve spinal fluid pressure in cases of chiari malformation.
What Are Potential Harms for Babies with Neural Tube Defects?
Even with aggressive treatments and surgery, there may still be some functional limitations in children with these defects. Those include:
- Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction.Some children will need long-term laxative use and catheterization because the nerves that help the bowel and bladder are affected.
- Lower Limb Dysfunction.Many kids that live with spina bifida need to use a wheelchair because they have trouble walking. This also requires physical therapy and occupational therapy to help improve function and teach them to perform daily activities.
- Headaches. Because of spinal fluid build-up, many kids that suffer chiari malformation suffer debilitating headaches. Doctors can place a shunt to help the fluid drain, but they may require medications to relieve the headaches.
- Learning Delays.Some children will need special education for learning disabilities and delays. A few children are even mentally retarded with some of these conditions. Intellectual difficulties can even set in later in childhood and need to be addressed and treated.
- Seizures.If the spinal fluid builds up too high in the brain, seizures can result. This issue is treated with shunting and/or seizure medications.
There can be other issues and the treatments are aimed to relieve symptoms and improve the child’s quality of life.
How to Prevent Neural Tube Defect
The majority of cases of neural tube defects can be prevented if women of childbearing age get enough folic acid in their diet prior to and in the early weeks of pregnancy. Studies show that getting enough folic acid can help the healthy development of the neurological system which happens before a woman even knows she is pregnant prior to the 4th week of pregnancy.
Government regulations in the United States now require that food manufacturers fortify all grain products with folic acid. This includes cereals, whole grain breads, and pasta. Since foods have been fortified, there has been a 46% reduction in neural tube defects.
Women who do not eat fortified grain products should be getting at least 400 mcg of folic acid a day from a supplement if they are of childbearing age. Pregnant women who do not eat fortified grains need more from supplement and should consult a doctor for the actual dosage. A woman who has a history of neural tube defects in the family or previously had a child with these defects needs to be extra careful about getting enough folic acid in any future pregnancies.
